

- Shadowsocks client 配域名 install#
- Shadowsocks client 配域名 update#
- Shadowsocks client 配域名 password#
- Shadowsocks client 配域名 Pc#
Shadowsocks client 配域名 install#
Use the Teddysun script to install Shadowsocks-Libev on the server: wget chmod +x shadowsocks-libev-debian.sh. You will receive a 192-bit password, expressed as 32 base-64 characters, which looks like this: IMC/Coe/bkfXQw7nvqqCm3Q/RBGgp1j2 2.2.
Shadowsocks client 配域名 password#
Generate a strong password for Shadowsocks: openssl rand -base64 24
Shadowsocks client 配域名 Pc#
Test this by opening a browser on your PC and visiting the HTTPS version of your site. You now have a working HTTPS camouflage website with a few sample pages on it. apt install certbot python-certbot-nginx -y certbot -nginx certbot renew -dry-run Now we make the site accessible by HTTPS on port 443, following the instructions for Nginx and Debian 10 on the Certbot website. Using our example of a host named that would be: apt install wget zip unzip -y wget unzip master.zip cp -rf sample-blog-master/html/* /var/www/html/Īt this point, you can test to see if your host name resolves to your IP address by opening a browser on your PC and visiting the HTTP version of your site. You can add different content if you have some. Here is an example of how you might do that. Add Camouflage Content to Web ServerĪdd a few realistic webpages to your camouflage site. Restart Nginx for all your changes: nginx -t systemctl restart nginx 1.5. Insert the real server name, which in our example is server_name Immediately below that, insert lines that will allow only expected HTTP request methods: if ($request_method !~ ^(GET|HEAD|POST)$ )Īlso add a line to provide some realistic browser caching: expires 1h Then edit the default site definition file: vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default Therefore edit the main Nginx configuration file: vi /etc/nginx/nf We want to make the Nginx web site look as much as possible like a realistic production server.
Shadowsocks client 配域名 update#
Install the Nginx web server on your server: apt update & apt upgrade -y apt install nginx -y 1.4. Implement BBR TCP congestion control on your server with the following commands: cat > /etc/sysctl.d/nf < Under certain types of network congestion, it will improve your latency. Implement BBRīottleneck Bandwidth and Round-trip propagation time (BBR) is a TCP congestion control algorithm developed at Google. If you are not using nftables, then make the equivalent changes for your firewall. If you are using nftables, then enter the commands above. Whichever one you are using, you will need to open ports 80 and 443 for TCP input and persist your changes across reboots.įor example, if you are using nftables with a policy of drop on Debian 10+, the commands would be: nft add rule inet filter input tcp dport counter accept nft list ruleset > /etc/nf Open Firewallįirewalls are typically implemented with nftables, iptables, ufw, firewalld, or security groups. We end the tutorial by describing the procedure for setting up a Windows client. If your server or client runs a recent version of Ubuntu, the procedures will be very similar to those for Debian 10+. In the examples in this article, we give the server host name as and the server IP address as yy.yy.yy.yy. 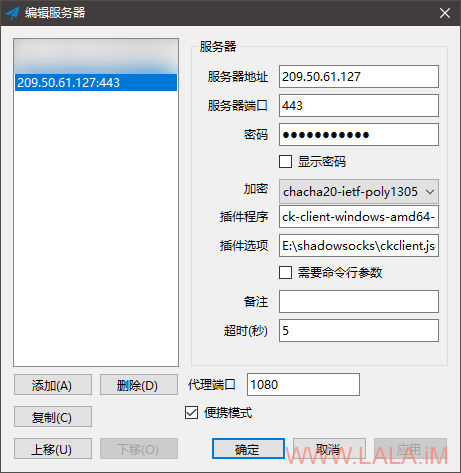


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
